
Facade Resilience Evaluation Framework
Resiliency is the capacity of a building (or building component in the case of the facade) to support building functionalities during extreme events

Resiliency is the capacity of a building (or building component in the case of the facade) to support building functionalities during extreme events
The stability of monolithic glass fins is reasonably well defined; as an elastic material it behaves in a similar manner to other elastic materials

Traditional approach for engineering the facade is building an isolated analysis model. However, it inhibits a dynamic design process where

Glass has become a popular building material that is used not only for windows but also as a load-bearing material. New dimensions of glass panes in
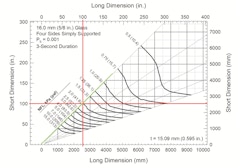
ASTM published the first version of ASTM E2461-05: Standard Practice for Determining the Thickness of Glass in Airport Traffic Control Tower Cabs in
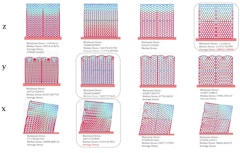
This research looks at the relationship of material and geometric distribution to set a methodology for integrating structural and thermal design.

Big data is having a noticeable impact on enclosure engineering design. With continuing advancements that liberate the geometrical form and the
As overall project schedules continue to contract and rising costs impact our design decisions, the importance of the design-assist phase for facades

The SCALP device is designed to measure the residual compressive surface stress of glass. As the SCALP does not rely on the birefringence properties
Other than limited special cases, there is a lack of standards providing guidance on the design of structural glass. This has resulted in an ad-hoc

Today’s environmental challenges highlight the necessity of a holistic approach to façade design and construction, key to achieve the ambitious 2030

In the very earliest stages of a design, an architect imagines a unique glazed facade form and wonders, “Is this possible?” and “What will it cost?”
Glass is an essential component for any type of building. Its transparency enhances daylighting and provides occupants a view to the outside. Whether

Building envelopes are not only an immediately visible part of the building, they have also become a major factor both for cost and performance of

The design of structural glass systems continues to evolve with the parallel development of new manufacturing technology. Improvements in the

ASTM E 1300 “Standard Practice for Determining Load Resistance of Glass in Buildings” defines the load resistance of a glass construction as being
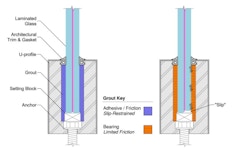
Effective thickness is a simplified method for the structural evaluation of laminated glass section properties. The method consists of defining the
Embodied carbon in buildings is a key factor in building decarbonization and while it is generally small compared to operational carbon, the

Fountain Place is a project that exemplifies the latest technology and applications in building skin design and jumbo structural glass applications,