24 results
-
The contemporary renovation of historic buildings often includes all-glass structures that allow architects to preserve the original building design…
-
Glass in GSA Buildings
- Paper by Georgia Scalfano, Technical Services Sustainability Manager
Embodied carbon in buildings is a key factor in building decarbonization and while it is generally small compared to operational carbon, the… -
A Structural Glass Design Manual
- Paper by Richard Green PE SE P.Eng CPEng IntPE(Aust) APEC Engineer · Terrence McDonnell S.E., P.E., P.Eng., SECB · Andrew Crosby BASc, P.Eng., LEED® AP BD+C
Other than limited special cases, there is a lack of standards providing guidance on the design of structural glass. This has resulted in an ad-hoc
-
Advanced Simulation for Thermal Stress Assessment
- Paper by Andrea Zani · Jamie Reyes · Guido Lori · Jacob Hanke · Giacomo Zangiacomi
In recent years, the desire for increased performance, transparency and visual flatness of glazing elements in curtain walls has generated renewed
-
Delivering Beauty
- Paper by Michael Mulhern,
Amidst the critical conversations about the need to build better and more efficient building skins, designers are also mindful of the need for the… -

Case Study: Renovation of Fountain Place
- Paper by Alfonso Lopez P.E., Principal and CEO David Dunham P.E, Director of Business Development Diarmuid Kelleher P.E., S.E., Director of Engineering
Fountain Place is a project that exemplifies the latest technology and applications in building skin design and jumbo structural glass applications,… -
Insulating Glass Unit Gas Loss
- Paper by Mark K. Schmidt, M.Eng., S.E. · Stephen M. Morse, PhD, P.E.
Concerns over time-dependent argon permeation through the perimeter edge seals of insulating glass units (IGUs) led the authors to utilize two
-
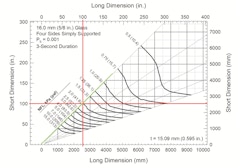
Control Tower Glass Design
- Paper by Daniel McCormick, P.E., PMP, M.ASCE · Stephen M. Morse, Ph.D., P.E., M.ASCE · Scott H. Norville, Ph.D., P.E., F.FTI, F.ASTM, F.ASCE
ASTM published the first version of ASTM E2461-05: Standard Practice for Determining the Thickness of Glass in Airport Traffic Control Tower Cabs in
-
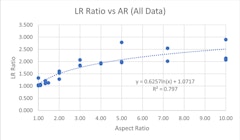
Fixed Edge Supports
- Paper by James G. Soules, Ph.D., P.E., S.E., P.Eng., SECB, F.SEI, F.ASCE · Stephen M. Morse, Ph.D., P.E., M.ASCE · Scott H. Norville, P.E., Ph.D.
Model building codes and standards in the United States use a probabilistic model to define glass load resistance (LR). In general, these model
-
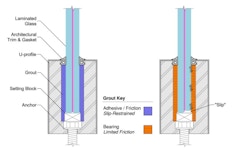
Laminated Security Glazing
- Paper by Vaughn Schauss,
Glass is an essential component for any type of building. Its transparency enhances daylighting and provides occupants a view to the outside. Whether… -

Addressing Embodied Carbon
- Paper by Helen Sanders, PhD, General Manager Adam Nizich, Senior Consulting Engineer
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions from the building sector is critical to limiting global temperature rise to less than 1.5⁰C. Construction and… -
Advances in Laminated Glass Engineering
- Paper by Richard Green PE (WA, NY, TX, CO, OR, MT), M.IEAUST CPEng, NER(Aus), APEC Engineer, IntPE(Aus), RBP(Vic)
The stability of monolithic glass fins is reasonably well defined; as an elastic material it behaves in a similar manner to other elastic materials
-
Advances in Effective Thickness
- Paper by Adam J Nizich, P.E. · Andrea M. La Greca, P.E. · Laura Galuppi, PhD
Effective thickness is a simplified method for the structural evaluation of laminated glass section properties. The method consists of defining the
-

Thermal Analysis of Complex Glazing
- Paper by Adrian Turcato · Chris Stutzki · Erik Olsen
The use of bidirectional scattering distribution function incorporated in a transient systems simulation program, allows engineers to accurately
-

Silicone Spandrel Glass Opacifiers
- Paper by Scott Norville, Samir Blanchet, George Torok, Kris Vockler, John Swanson, Chris Barry, Lawrence Carbary, Stephane Hoffman, Timothy Krytenberg, Chris Fronsoe,
Curtain wall design commonly uses insulating glass units for vision and spandrel glazing to provide better visual harmonization of building facade… -
Origami-Inspired Facade Design
- Paper by Joshua Schultz, Ph.D, P.E., LEED AP, ENV SP · Neil Katz, AIA
To paraphrase Robert le Ricolias, the art of the structure is where to put the folds. Using that inspiration, fundamental concepts from origami,
-

Glass and Electromagnetic Eavesdropping Protection
- Paper by Eric Stein
Glass is a key component in building design. Benefits of utilizing Insulating Glass Units (IGUs) within a building facade are well understood,
-

Design Considerations
- Paper by Stephen M. Morse, Ph.D. · Kayla Natividad, Ph.D. · H. Scott Norville, P.E., Ph.D.
Window glass design using ASTM E 1300 entails determining glass thickness(es) and types so that the window glass construction load resistance
-

Controlling Anisotropy in Heat Treated Glass
- Paper by Francis Serruys, Dr. Romain Decourcelle,
Anisotropy is also known as Brewster marks, quench marks, strain pattern, leopard spots, Iridescence, etc. Although anisotropy is inevitable when… -

Anisotropic Effects in Architectural Glass
- Paper by Luis M. Hidalgo · Michael Elstner
Iridescence effects, quench marks, leopard marks… The names given to optical anisotropy in toughened and heat-strengthened glass are diverse and
